Exercise is essential for maintaining overall health, even for individuals on oxygen therapy. In fact, regular physical activity can improve your cardiovascular health, increase your energy levels, and enhance your sense of well-being. But if you rely on supplemental oxygen, you might feel uncertain about how to incorporate exercise into your routine safely and effectively.
As a respiratory therapist with years of experience helping patients balance oxygen therapy and fitness, I’ve seen firsthand how beneficial and achievable exercising with oxygen therapy can be. In this article, I’ll share practical tips and strategies to help you stay active while maintaining your oxygen needs.
The Benefits of Exercising with Oxygen Therapy
Using oxygen therapy during exercise allows you to maintain proper oxygen levels, which is crucial for avoiding breathlessness and fatigue. Benefits include:
- Improved Lung Function: Regular exercise helps strengthen the respiratory muscles.
- Enhanced Stamina: Better oxygenation supports longer and more effective workouts.
- Boosted Confidence: Staying active can reduce the mental and physical limitations associated with oxygen therapy.
1. Consult Your Healthcare Provider
Before starting any exercise program, it’s essential to discuss your plans with your doctor or respiratory therapist.
Key Questions to Ask:
- Is it safe for me to exercise while using oxygen therapy?
- What types of exercises are suitable for my condition?
- Do I need to adjust my oxygen flow rate during exercise?
Your doctor may recommend a pulmonary rehabilitation program to help you start exercising safely under supervision.
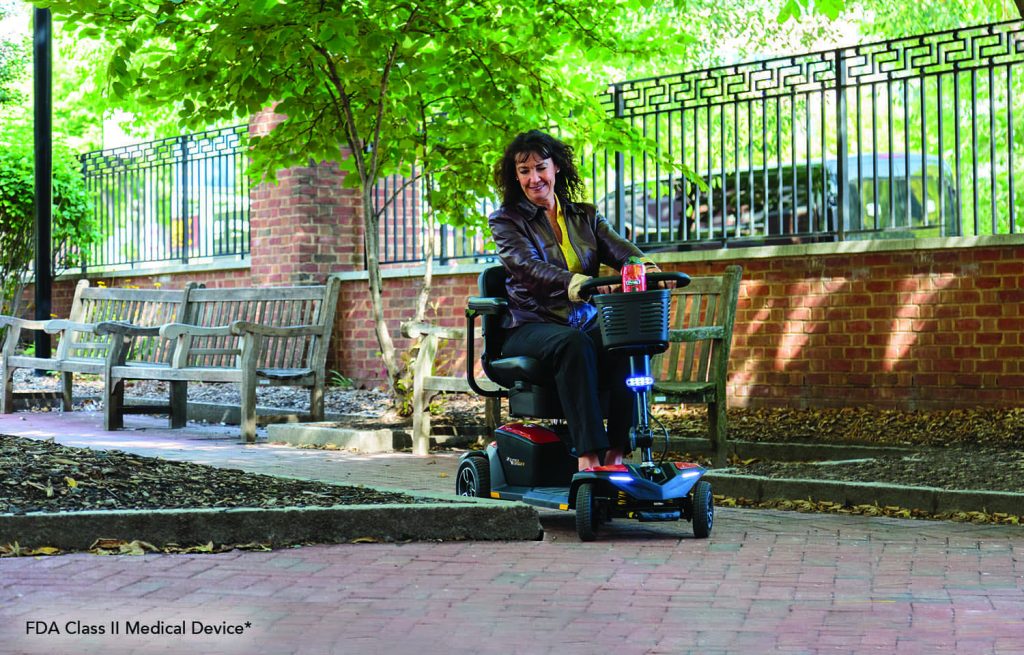
2. Choose the Right Equipment
Having the right oxygen equipment can make exercising more comfortable and convenient.
Portable Oxygen Options:
- Portable Oxygen Concentrators (POCs): Lightweight and easy to carry, many POCs come with straps or backpacks designed for mobility.
- Oxygen Tanks with Carts: If you use an oxygen tank, consider a wheeled cart for easier movement.
- Nasal Cannulas: Use a flexible and lightweight cannula to avoid discomfort during activity.
Tips for Equipment Use:
- Test your device before exercising to ensure proper function.
- Use tubing clips or fasteners to secure tubing and prevent it from tangling.
3. Start Slow and Build Gradually
If you’re new to exercising with oxygen therapy, start with low-impact activities and gradually increase intensity as your stamina improves.
Beginner-Friendly Exercises:
- Walking: Start with short distances and gradually increase your pace and duration.
- Chair Exercises: Seated exercises like leg lifts or arm raises are great for building strength.
- Stretching: Gentle stretches improve flexibility and reduce stiffness.
4. Monitor Your Oxygen Levels
Maintaining adequate oxygen levels during exercise is crucial for your safety and effectiveness.
How to Monitor:
- Use a pulse oximeter to track your oxygen saturation (SpO2). Aim to keep levels above 88-90%, or as advised by your doctor.
- Stop exercising if you feel dizzy, lightheaded, or excessively short of breath.
Adjusting Oxygen Flow:
- Your doctor may recommend increasing your oxygen flow rate during exercise.
- Never adjust your flow rate without consulting your healthcare provider.
5. Practice Breathing Techniques
Proper breathing techniques can enhance your oxygen efficiency and reduce breathlessness during exercise.
Techniques to Try:
- Pursed-Lip Breathing: Inhale through your nose for two counts, then exhale slowly through pursed lips for four counts.
- Diaphragmatic Breathing: Focus on expanding your diaphragm as you inhale deeply.
These techniques can help you manage shortness of breath and maintain a steady rhythm during workouts.
6. Stay Hydrated and Dress Comfortably
Hydration and clothing play a vital role in your exercise routine.
Hydration Tips:
- Drink water before, during, and after your workout to prevent dehydration.
- Avoid caffeinated or sugary drinks, which can dehydrate you.
Clothing Tips:
- Wear loose, breathable clothing to stay comfortable and avoid restricting movement.
- Choose footwear with good support to prevent strain on your joints.
7. Incorporate Strength and Flexibility Training
In addition to cardio exercises, include strength and flexibility workouts in your routine.
Strength Training:
- Use resistance bands or light dumbbells for exercises like bicep curls or seated rows.
- Perform 2-3 sessions per week to build muscle and improve overall strength.
Flexibility Training:
- Incorporate stretching or yoga to enhance flexibility and reduce muscle tension.
- Focus on gentle movements to avoid strain or discomfort.
8. Cool Down and Recover
Ending your workout with a proper cool-down routine helps your body recover and prevents sudden drops in oxygen levels.
Cool-Down Routine:
- Spend 5-10 minutes doing light stretches or walking at a slower pace.
- Practice deep breathing to relax your muscles and regulate your heart rate.
9. Overcome Mental Barriers
Exercising with oxygen therapy can feel intimidating at first, especially in public spaces.
How to Build Confidence:
- Start exercising at home before moving to public spaces.
- Bring a friend or family member for support and encouragement.
- Remind yourself that using oxygen is a sign of strength and commitment to your health.
FAQs
1. Can I exercise with oxygen therapy if I have COPD or another lung condition?
Yes, exercising can be beneficial for many lung conditions. Consult your healthcare provider to create a safe and effective plan tailored to your needs.
2. What should my oxygen saturation levels be during exercise?
Most doctors recommend keeping SpO2 levels above 88-90%. Use a pulse oximeter to monitor your levels regularly.
3. Are there any exercises I should avoid?
High-impact or strenuous activities that leave you excessively breathless may not be suitable. Focus on low-impact options like walking, swimming, or yoga.
4. How long should I exercise each day?
Start with 10-15 minutes and gradually increase to 30-45 minutes, depending on your fitness level and doctor’s advice.
5. Can I exercise outdoors with oxygen therapy?
Absolutely! Outdoor activities like walking in a park can be refreshing and enjoyable. Ensure your equipment is portable and the weather is suitable.
Conclusion: Staying Active with Oxygen Therapy
Using oxygen therapy doesn’t have to limit your ability to exercise—it can enhance your ability to stay active safely and effectively. By starting slow, monitoring your oxygen levels, and choosing the right activities, you can enjoy the many physical and emotional benefits of regular exercise.
Remember, the key is to listen to your body and work closely with your healthcare team. With the right approach, you can stay healthy, improve your stamina, and enjoy a more active lifestyle.